Course Project

Developing an generative AI bias reporting tool based on user research, design and testing.
Role
UX Researcher
Timeline
12 Weeks
Skills
Prototyping
Storyboard
Interviews
Affinity Diagram
Task Flow
User Tests
Tools
Figma
Miro
Gemini
ChatGPT
Team
Elin Jiang
Emma Im
Kat Karl

Exploration
The Problem
Biased algorithms can reinforce existing societal prejudices, and those who may not flag bias in artificial intelligence risk perpetuating this inequality.
Currently, there is a lack of open platforms where people can voice their everyday encounters with bias online, and especially a platform where they can see others’ interactions with them as well.
As our reliance on AI intensifies, it becomes imperative to ensure fairness and equity in the design and deployment of these technologies. We must prioritize the development of generative AI systems that are not only technologically advanced but are also shaped by an ethical commitment to inclusivity and equity.
— Zhou et al. 2024
Exploration
The Current Model
CMU HCII professor, Dr. Hong Shen, developed the application WeAudit TAIGA as a tool to highlight and report biases in generative AI. We decided address the pain points of the tool through user research and create a solution that is usable and engaging.
Exploration
Usability Tests
To highlight pain points, these tests followed a direct, straight-forward framework to follow instructions and ensure that the basic functionalities are executable.

1. Users experienced confusion on where to go each time they were assigned with the task: the UI of the interface was not self-explanatory nor straightforward.

2. Log-in process was not as clear and required much navigation back and forth.

3. The "create thread", "image generation" and "report" functionalities were confused with the report button.
The ratio of negative to positive occurrences during the testing process was 17:5, and there were 3 neutral insights.
There seemed to be confusion for both the participants and the test administrators regarding the appearance/disappearance of the threads feature.
Users need more clarification or a more direct overview/guide that would allow them to develop an understanding of the outcome of the website and how they can navigate/flow through the website.
Exploration
Heuristic Evaluation
I used the heuristic evaluation principles to flag areas of the interface that do not match guidelines.
Visibility of System Status
Presence of two search bars - unclear whether search has been made or not

Help and Documentation
Three-step documentation for generating images, no resource to troubleshoot

User Control and Freedom
Once generating an image, there is no way to save the thread or return to main page

User Control and Freedom
Users can name threads, tag them, and provide description before posting

So how might we...
Ensure that users can utilize their diverse backgrounds and experiences to evaluate bias in AI generated images to effectively frame an argument about AI bias.
User Research
User Survey Analysis
From a large survey with over 1000 participants, I examined how exploring AI image generation interfaces can surface biases in the outputs and how users felt about these biases.

Perceptions of bias in generative AI outputs are significantly higher among minority groups, with 45% more individuals identifying the results as generally harmful compared to the majority group.

There was a consistent distribution of responses across gender categories, indicating a widespread awareness and concern about the potential harm of gender bias in generative AI outputs.
User Research
Consolidating Research
In order to “Walk The Wall” I initially took a look at our previous work on developing a background understanding on generative AI, looking at how I could visualize data regarding generative AI biases and user representations.

Key Takeaways
Parallel functionality to social media platforms for intuitive use
Provide guidance and a statement of purpose to calibrate user’s approach to the website
Feedback and efficiency with the UI
Keep the interface simple, cohesive and engaging
User Research
Learning About Our Users
At this point, I wanted to better understand the motivations and experiences that users have going into use cases of generative AI. I conducted user interviews to develop a persona and user profile.
Methods: Directed Storytelling, Semi-Structured Interview

INSIGHT 1: Bias recognition increases with firsthand experiences

INSIGHT 2: Biases in AI reflect existing societal issues

INSIGHT 3: Social media can exacerbate and educate bias in AI

INSIGHT 4: Solutions can be found in transparency

INSIGHT 5: Reporting bias in AI tools is not simple
Design
Defining the Product

To ensure that users can utilize their diverse background and experiences to evaluate bias in AI generated images to effectively frame an argument about AI bias through the website/service.
Goal

Form
A more accessible and navigable interface - such as an app in the form of social media to engage users and incentivize sharing and communicating.
Design
Sketches

Design
Wireframes

Design
User Tests
POSITIVES
-
Most users thought that our buttons were very clear and that uploading an image, comparing prompts, and using a prompt to generate an image were all straightforward tasks
-
User found the reporting feature as intuitive and accessible
TO WORK ON
-
Suggested adding a side-by-side comparison feature for original and AI-generated images to easily spot discrepancies or biases.
-
There was some uncertainty regarding what exactly they would flag as being biased and what they should consider as being biased
Design
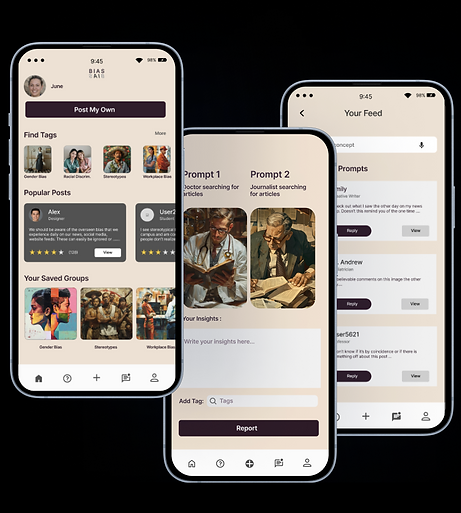
Final Prototype





Design
High Fidelity Designs

Reflection
What I Learned
Working With Teams
How best to handle differences in design choices, or interpretation of data
Time management and organizing schedules
Deep Dive into the User
Multiple methods simultaneously to get a better sense of use-cases
Compile notes from different models, or evaluation metrics to figure out how to make sense of the information
Effective Testing
Anticipate questions that the participant may have during testing
Reflection
With More Time

Conduct more usability tests to see what more improvements could be made to the flow of the website, especially the interaction with the community pages.

Explore different platforms, such as a website redesign, a tool - browser or website add-on. Integrating bias reporting on multiple platforms is important.

Implement a feedback method so that users are notified how their reporting is being used to make changes and prevent further bias in generative AI platforms.